
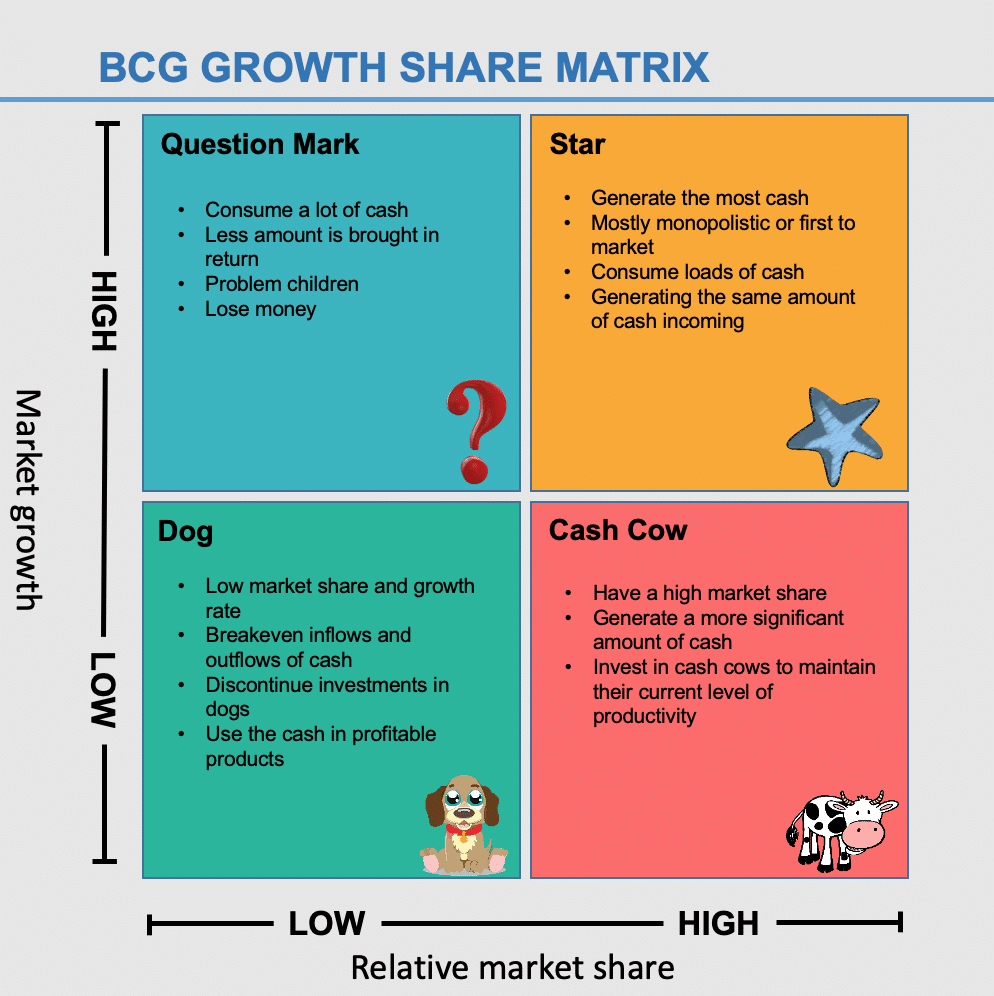
They are well established in their target market and require very little investment to hold their market share. They are low growth, high market share businesses products. Over the period of time their phase of growth will slow down and they will turn into cash cows. They will be the market leader of their industry or category. They need heavy investments to sustain their rapid growth. Stars are high growth, high share businesses or products. The growth-share matrix defines four types/quadrants of SBUs: Stars: The matrix consists of the market growth rate on the x-axis and relative market share on the y axis.

It helps identify the most promising sectors for expansion or reduction in relative market share. It is the best way to compare a company’s business units against each other, as opposed to comparing individual portfolio of products. Companies that are in the business of providing goods and services can use this tool to understand how they can improve their productivity, efficiency, and profitability. It can also help them reduce costs, improve productivity, and increase value creation in the long run. The BCG growth-share matrix can be used to identify and prioritize projects and evaluate the profitability of each product portfolio. It allows companies to understand how their strategic business units’ competitive advantage will impact future profit performance. This means that it can be used by companies with different cash flows and profit margins.
It does not require a company’s cash flow or profit as inputs. The BCG growth-share matrix is one of the few analytical tools that has been shown to be predictive and useful for investors to do portfolio analysis. It allows companies to see how market share can be expanded in certain markets, while others are reduced. It is a portfolio planning method, first developed by the Boston consulting group (founded by Bruce Henderson), that evaluates a company’s strategic business units in terms of market growth and relative market share.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
